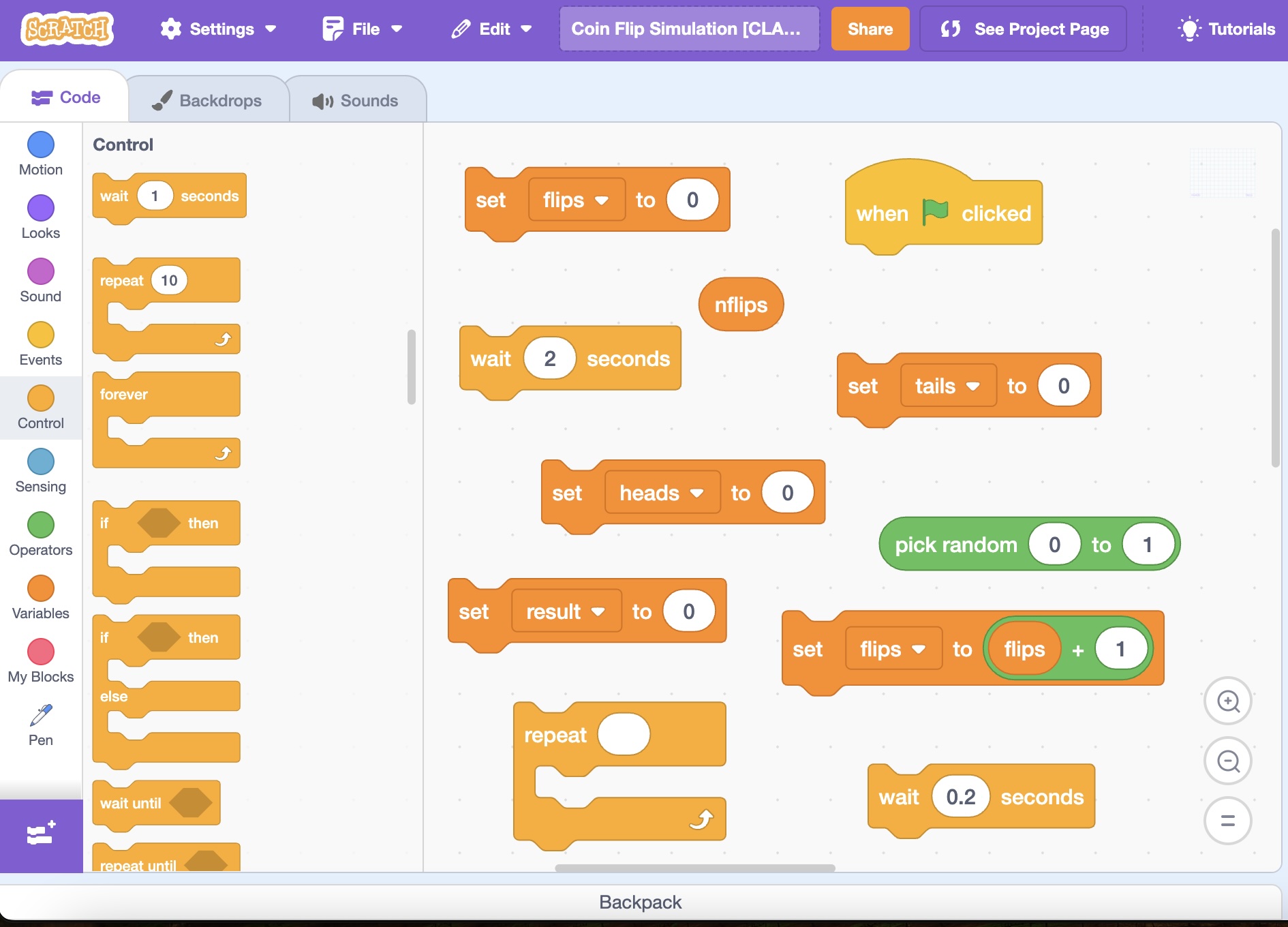
Variables and Main Loop
This animation displays a simulation of 500 coin tosses. As can be observed, the percentages of heads and tails are converging towards 50%, which is the theoretical probability of getting a head or a tail in a single toss.
0. Heads or Tails
Obviously, we need coins for this simulation. Coin flipping, coin tossing, or heads or tails is the practice of throwing a coin in the air and checking which side is showing when it lands, in order to choose between two alternatives, heads or tails, sometimes used to resolve a dispute between two parties.
1. Definition of variables
These are the variables that need to be defined in the simulation application:
Heads or tails?
result: This variable stores a random integer between 0 and 1, meaning result can have a value of 0 or 1. We will assign the value 0 to "heads" and the value 1 to "tails."
Number of heads and tails
heads: The variable heads stores the number of heads that have appeared so far.tails: The variable tails stores the number of tails that have appeared so far.
Flips or tosses
flips: The variable flips stores the number of heads and tails that have appeared so far, in other words, the number of coin tosses performed.nflips: The variablenflipsstores the number of tosses the simulator will perform.
Frequency and percetages
f_heads: The variablef_headsstores the percentage of heads that have appeared so far. It is a numerical value.f_tails: The variablef_tailsstores the percentage of tails that have appeared so far. It is a numerical value.p_heads: The variablep_headsstores the percentage of heads that have appeared so far followed by the "%" character. It is a text value displayed in the interface.p_tails: The variablep_tailsstores the percentage of tails that have appeared so far followed by the "%" character- . It is a text value displayed in the interface.
2. The Main Loop
The structure of the main program should look like this:
wait 2 sec
flips = 0
heads = 0
tails = 0
repeat nflips
result = random(0,1)
flips = flips + 1
wait 0.2 sec
In Scratch, you can build this main loop using the following instructions and control structures: