Digital Devices and Health¶
Introduction¶
Digital device use can lead to eye strain, headaches, and back pain due to poor posture and prolonged screen exposure. To prevent discomfort, adjust screen height, reduce glare, and take regular breaks. Blinking often helps avoid dry eyes.
Headaches are common due to close screen proximity and can be alleviated by stretching and maintaining good posture. Back pain can be reduced by practicing dynamic sitting, adjusting backrests, and using lumbar support.
Ergonomics plays a crucial role in optimizing equipment design to enhance comfort and efficiency, reducing strain and promoting overall health in work and living spaces.
How digital devices affect our bodies¶
Using digital devices affects our bodies. Here are some common effects:
-
Eye Strain: When we look at screens for a long time, our eyes can become tired. This is called "eye strain." It can make our eyes hurt, feel dry, or blurry. To avoid this, remember the "20-20-20 rule": every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
-
Sleep Problems: The light from screens (especially at night) can make it hard for us to sleep. Our brains need darkness to know when it’s time to rest. Avoid using screens at least one hour before bed to help your brain relax.
-
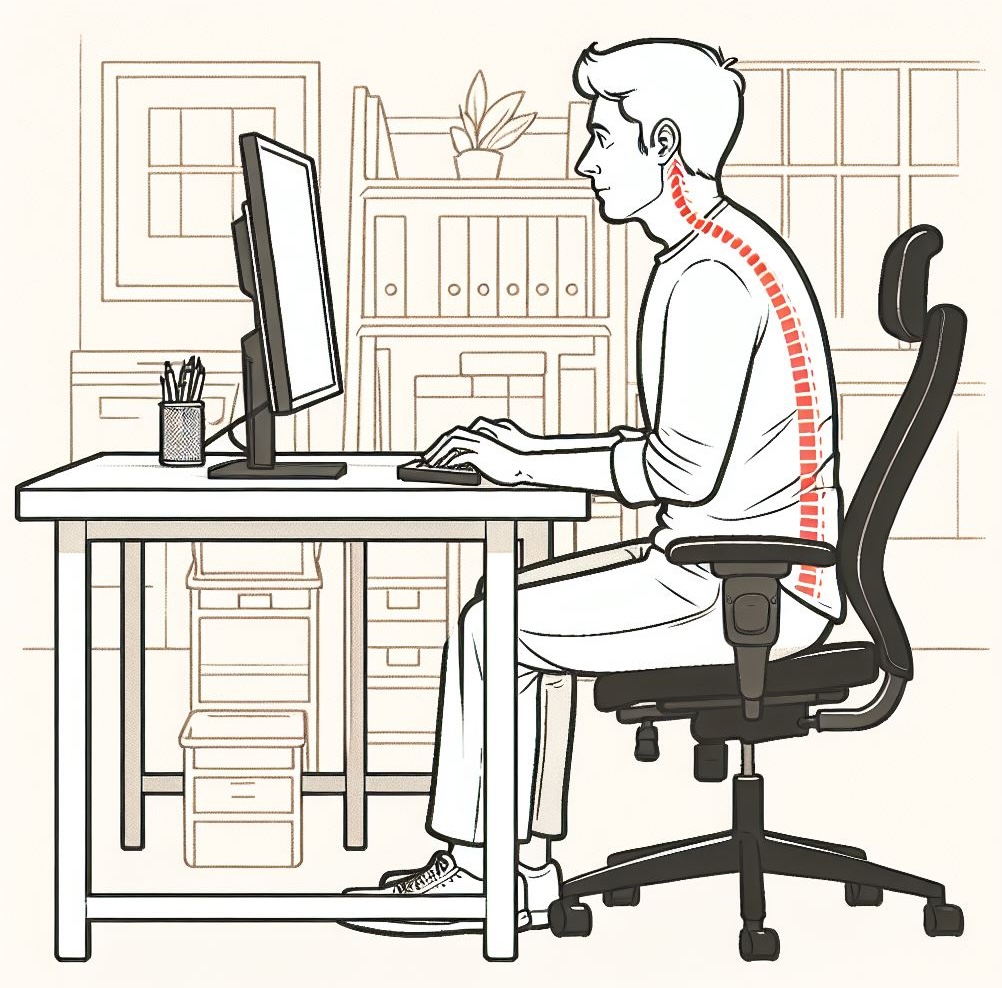
Bad Posture: When we use devices for too long, we may hunch over, which is bad for our neck and back. Try to sit up straight and take breaks to move around.
-
Less Physical Activity: Spending too much time on screens means less time being active, which is important for staying healthy. Balance screen time with physical activities, like playing outside or doing sports.
Risks and Tips¶
Eyestrain¶
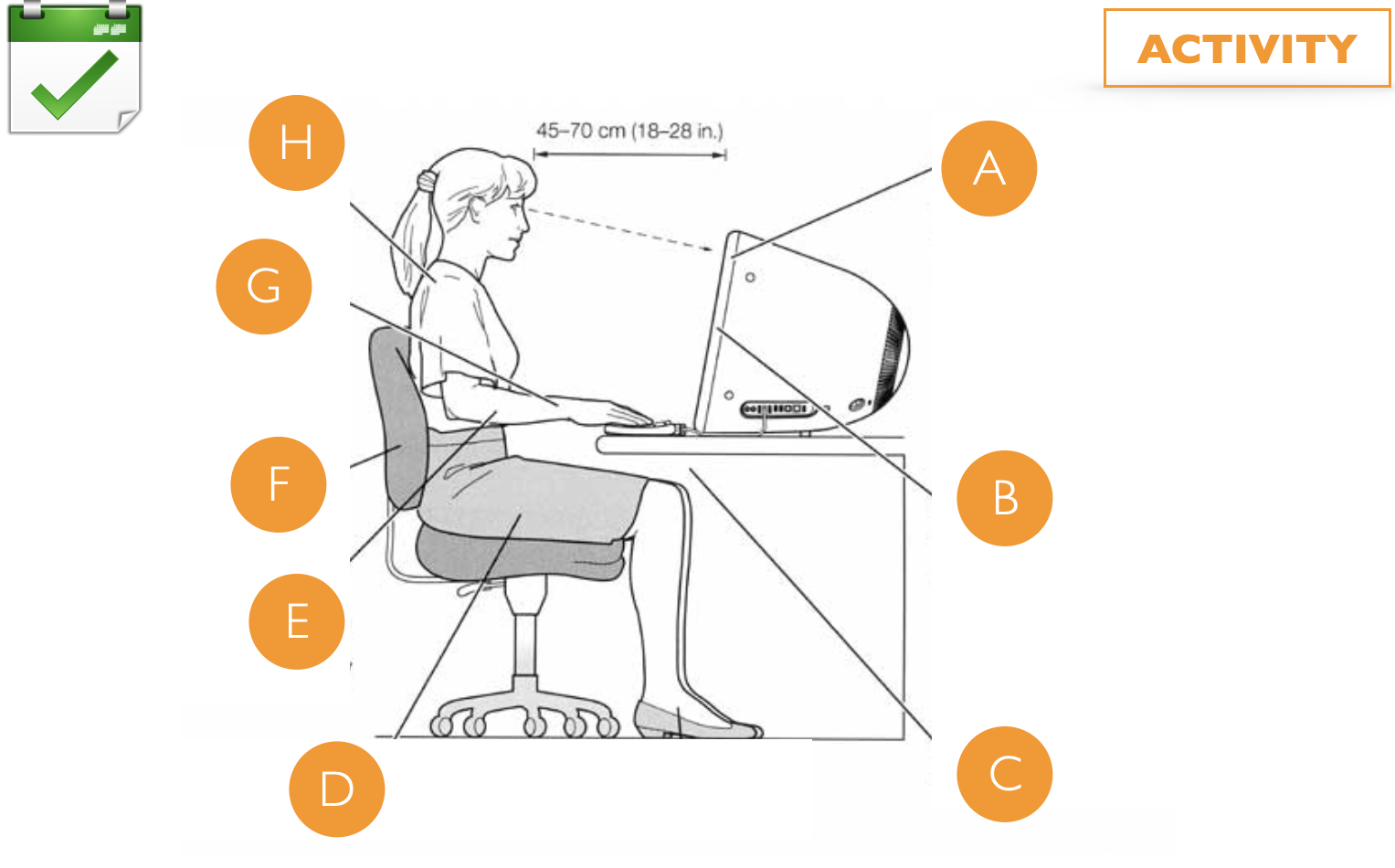
Computer users may experience symptoms such as blurred vision, temporary inability to focus on faraway objects and headaches.
- Computer screen - Adjust the height of your screen so you're not tilting your head down and tensing your neck.
- Lighting - Try adjusting the screen and the lights to keep glare to a minimum.
- Rest breaks - Taking periodic breaks, during which you relax and gently stretch your neck muscles, can ease muscle strain.
- Remembering to blink can help you avoid dry eyes
Headache¶
A computer screen is much like a television but you sit much closer to it. The light coming from the monitor can cause eyestrain if you stare at it for too long. This and also other reasons when working at a computer, including stress and poor posture can lead to a headache.
Regular breaks can help reduce muscle strain and alleviate these problems.
Backpain¶
While working at the computer, back pain is one of the most common workplace problems.
- Practice «dynamic sitting»: be flexible and move while sit, don’t just stay in one static posture.
- Adjust the backrest so you are sitting at a 90 degree angle.
- Adjust the lumbar support to fit your low back's natural inward curve.
- Adjust the height of the backrest to support the natural inward curvature of the lower back. Use your armrests.
Ergonomics¶
What is ergonomics?¶
Ergonomics is the scientific study focused on optimizing the design of equipment, tools, and workspaces to enhance efficiency, comfort, and safety.
It involves understanding human anatomy, behavior, and limitations to create environments and products that align with the body's natural movements and capabilities.
For instance, in office settings, ergonomic principles guide the design of chairs, desks, and computer setups to reduce strain on the neck, back, and wrists, thereby preventing repetitive stress injuries and promoting good posture. Similarly, in transportation, ergonomic seating aims to provide both comfort and safety, reducing fatigue during long journeys.
By considering factors like body posture, movement, and the reduction of physical strain, ergonomics not only improves productivity but also enhances overall well-being.
Activity¶
Ergonomics: Office, Laptop and Smartphones¶
Laptop Ergonomics - Basic Tips
Ergonomics: Smartphones & Tablets
Computing Health and Safety
Work safely in your office
This field draws on knowledge from disciplines such as biomechanics, psychology, and engineering to create user-friendly solutions that cater to the needs of diverse populations, ultimately contributing to healthier and more sustainable work and living environments.
Glossary¶
| English | Spanish | Example (Inglés) |
|---|---|---|
| Active | Activo | Stay active to counteract screen time. |
| Alleviate | Aliviar | Breaks alleviate muscle strain. |
| Anatomy | Anatomía | Anatomy plays a role in ergonomic design. |
| Armrests | Reposabrazos | Adjust the armrests for comfort. |
| Back pain | Dolor de espalda | Proper posture reduces back pain. |
| Balance | Equilibrar | Balance screen time with exercise. |
| Bedtime | Hora de dormir | Avoid screens near bedtime. |
| Behavior | Comportamiento | Digital behavior affects health. |
| Blinking | Parpadeo | Remember to blink regularly. |
| Body posture | Postura corporal | Correct body posture prevents pain. |
| Chair | Silla | Use an ergonomic chair for comfort. |
| Comfort | Comodidad | Ergonomics improve comfort and safety. |
| Computer setup | Configuración del ordenador | Adjust the computer setup for better posture. |
| Darkness | Oscuridad | Darkness helps the brain relax at night. |
| Desk | Escritorio | Keep your desk organized and ergonomic. |
| Digital device | Dispositivo digital | Digital devices impact eye health. |
| Discomfort | Incomodidad | Discomfort arises from poor posture. |
| Efficiency | Eficiencia | Efficiency is increased with ergonomic practices. |
| Equipment design | Diseño de equipos | Equipment design affects comfort. |
| Ergonomics | Ergonomía | Ergonomics improves workplace health. |
| Eyes | Ojos | Staring at screens strains your eyes. |
| Eye strain | Fatiga visual | Eye strain occurs with prolonged screen use. |
| Fatigue | Fatiga | Fatigue is common from extended screen exposure. |
| Flexibility | Flexibilidad | Flexibility in sitting reduces pain. |
| Glare | Deslumbramiento | Reduce glare for better visibility. |
| Headache | Dolor de cabeza | Headaches may follow long screen exposure. |
| Hunch over | Encogerse | Avoid hunching over while using devices. |
| Inward curve | Curvatura interna | Adjust lumbar support for inward curve of the back. |
| Lighting | Iluminación | Proper lighting reduces glare. |
| Lumbar support | Soporte lumbar | Lumbar support helps avoid back pain. |
| Monitor | Monitor | Adjust your monitor height for comfort. |
| Move around | Moverse | Move around to prevent muscle strain. |
| Muscle strain | Tensión muscular | Take breaks to prevent muscle strain. |
| Neck | Cuello | Neck pain can result from poor posture. |
| Physical activity | Actividad física | Physical activity balances screen time. |
| Posture | Postura | Good posture prevents digital strain. |
| Productivity | Productividad | Productivity is boosted by ergonomic designs. |
| Relax | Relajarse | Relax your eyes after screen use. |
| Rest break | Descanso | Take rest breaks to avoid strain. |
| Safety | Seguridad | Safety is enhanced by ergonomic practices. |
| Screen height | Altura de la pantalla | Adjust screen height to avoid neck strain. |
| Stretching | Estiramiento | Stretching relieves muscle tension. |
| Stress | Estrés | Stress can result from poor ergonomics. |
| Sustainable | Sostenible | Sustainable ergonomics support long-term health. |
| Television | Televisión | Television is similar to using digital devices. |
| User-friendly | Fácil de usar | Ergonomics ensures user-friendly setups. |
| Workspace | Espacio de trabajo | Ergonomic workspace designs improve comfort. |
| Wrist | Muñeca | Wrist pain can be caused by poor posture. |